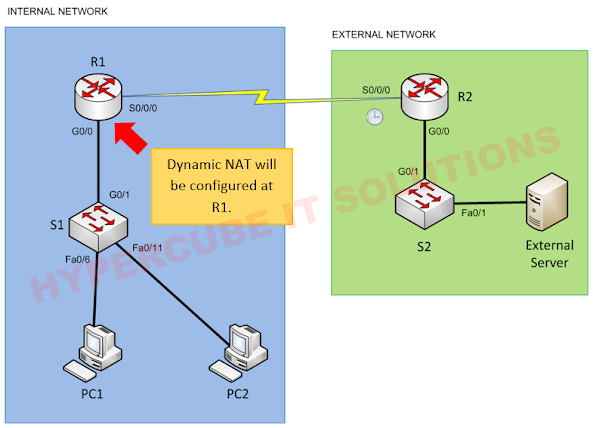
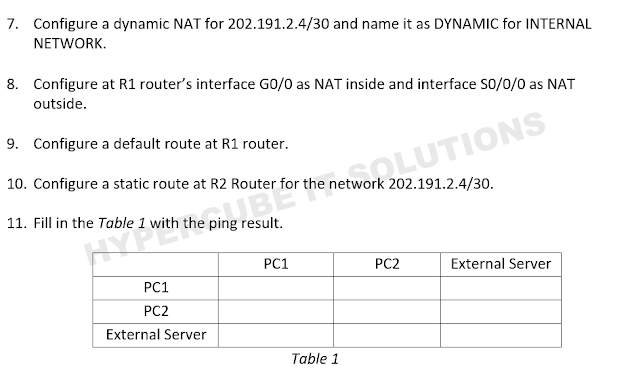
A router is a network device that forwards data packets between computer networks. We need to configure routing on the router, so that it can select the best path to transfer the data packet from source to destination.
In this lesson, we will explain how to configure static and default route on the router.
We have Network A, B and C, as shown in the figure below.
We will configure default route on R1 and R3.
We will configure static route on R2.
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no shutdown
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.10
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.20
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.2
R2 Configuration
hostname R2
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 20.20.20.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1
ip route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1
ip route 192.168.30.0 255.255.255.0 20.20.20.1
R3 Configuration
hostname R3
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 20.20.20.2
S1 Configuration
vlan 10
name Net-A
vlan 20
name Net-B
interface FastEthernet0/1
switchport access vlan 10
switchport mode access
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport access vlan 20
switchport mode access
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20
switchport mode trunk
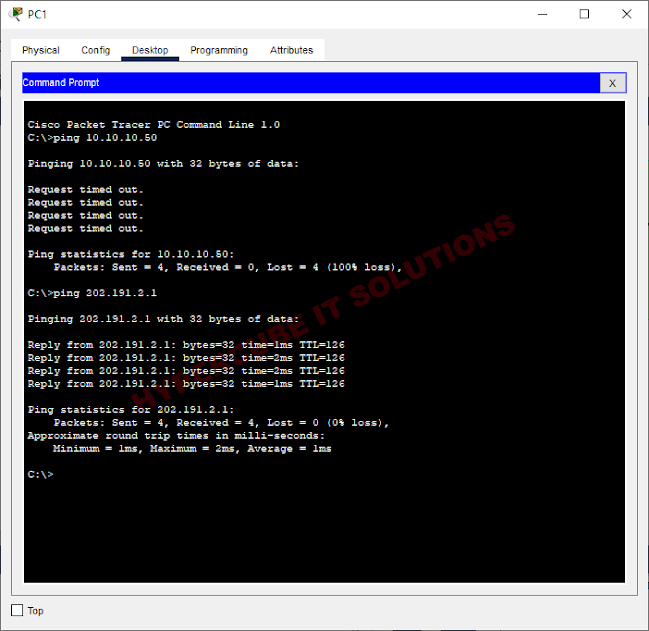
All devices can ping with each other.